Monarda Gardening[an error occurred while processing this directive][an error occurred while processing this directive] | ||||||
|
Monarda is a genus of flowering plants in family Lamiaceae, comprising 16 species. It is indigenous to North America. It is commonly known as bee balm, horsemint, oswego tea, or bergamot. The genus name was named for Nicolas Bautista
Monardes ( 1490 - 10 Oct 1588), a Spanish physician and botanist, who wrote a book in 1574 describing plants found in the New World. The plants are widespread across North America and can be found in moist meadows, hillsides, and forest clearings up to 1500 m in elevation. The showy, long-lasting flowerheads of Monarda are carried on erect stems from mid- to late summer. They are excellent in mixed borders and in wildlife gardens. Monarda is a natural source of antiseptic Thymol, the primary active ingredient in modern commercial mouthwash formulas. Although somewhat bitter, due to the thymol content in the plant leaves and buds, the plant tastes like a mix of spearmint and peppermint with oregano. Monarda species are annual and perennial upright growing herbaceous plants. It has lanceolate to oval shaped leaves, and flowers are borne in dense profusion at the end of the stem and/or in the stem axils. The flowers are typically crowded into head-like clusters with leafy bracts. Flower colors vary from shades of red, pink and purple. There are over 50 commercial cultivars and hybrids, ranging in color from candy-apple red to pure white to deep blue, but these plants tend to be smaller than wild species, and often develop to combat climatic or pest conditions. Other have been developed to produce essential oils for food, flavoring and medicine. Monarda didyma (Oswego tea, sweet bergamot), 90 x 45 cm, which is often grown in herb gardens, is parent to many hybrids. It has red-pink flowers surrounded by reddish bracts and mid-green leaves. M. 'Beauty of Cobham' has pale pink flowers with purple pink bracts. M. 'Cambridge Scarlet' has red flowers and plum red bracts. Monarda is often used in beds and borders to encourage and increase the appearance of hummingbirds and pollinating insects. Plant Monarda in full fun, in fertile, moisture-retentive but well-drained soil. Propagation is by seed or by division in spring. the plant should be divided every 3 -5 years to reduce spread, keep the central core of the plant healthy, prelude root rot, and also increase air circulation about the foliage. Pests are slugs and snails.  Monarda didyma Author: Beentree (Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.5 Generic)  Monarda didyma Author: Beentree (Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.5 Generic)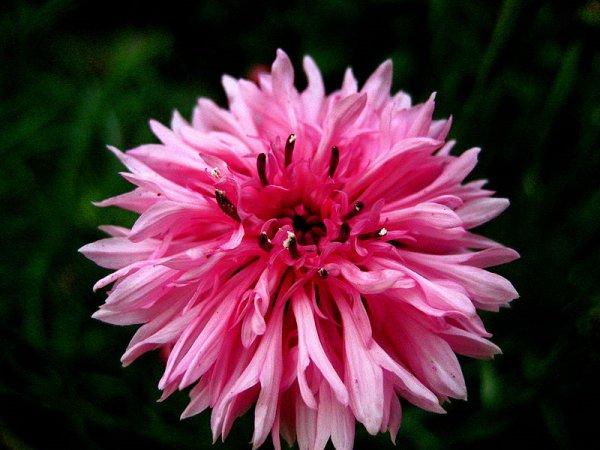  Monarda didyma Author: Stef1432 (GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2) Monarda punctata Author: Ted Bodner (Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 3.0-unported)  Monarda citriodora Author: Eugene van der Pijll (public domain)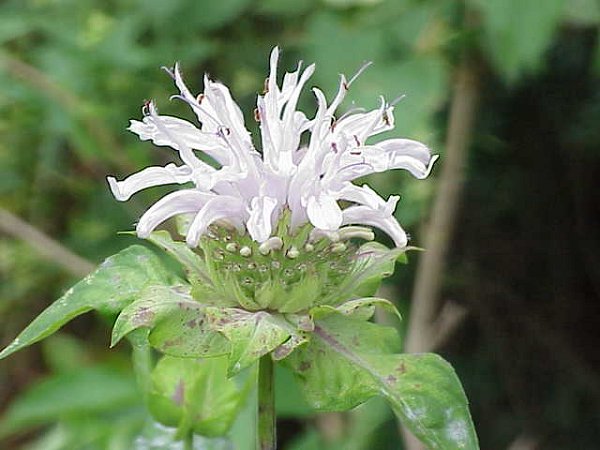  Monarda fistulosa Author: Kurt Stueber (Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 3.0)  Monarda hybrida Author: Dy-e (Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.5 Generic)  Monarda fistulosa seedhead Author: PDH (public domain)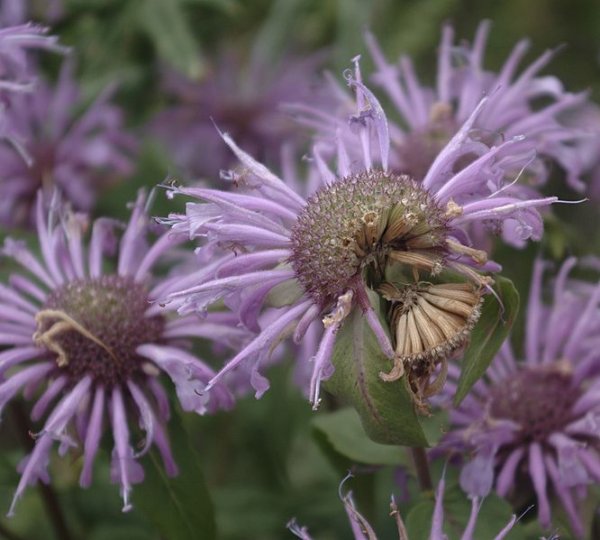  Monarda menthifolia Author: JerryFriedman (Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 3.0-unported) | ||||||
|